Introduction:
Modern technology would not be complete without LCDs. Digital watches, computer displays, cellphones, and TVs are just a few of the devices that include them. An LCD is a kind of flat-panel display that uses liquid crystals to produce pictures. In this blog, we’ll discuss the principles of LCD technology, numerous LCD kinds, their advantages and disadvantages, and the future of LCDs.
Basic Principle of LCDs:
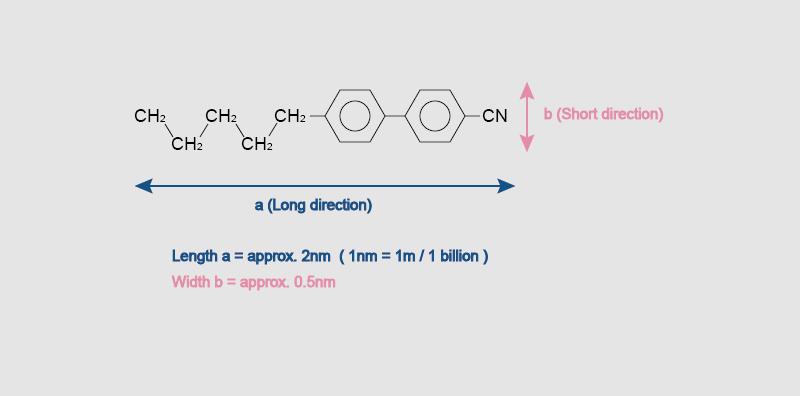
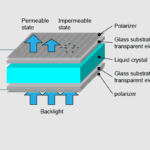
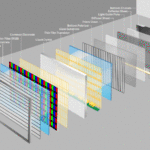
Liquid crystal is the key component of LCD technology. The phrase “liquid crystal” describes a specific kind of substance that combines the characteristics of solids and liquids. They have the capacity to polarise light, which modifies how light waves traverse them. Two liquid crystal layers and two polarising filters make up an LCD. The polarisation of the light passing through the liquid crystal is altered when a voltage is applied, which causes the display of an image.
Types of LCDs:
Today’s market is home to a variety of LCD models. Twisted Nematic (TN), In-Plane Switching (IPS), and Vertical Alignment (VA) LCDs are the three most popular types.
The most popular kind of LCD is a TN LCD. They are perfect for applications that need quick image rendering because they are reasonably priced and have a quick response time. However, the viewing angles and colour reproduction of TN LCDs are constrained, which can lead to subpar image quality.
Although more expensive than TN LCDs, IPS LCDs have wider viewing angles and better colour reproduction. Additionally, because of their slower reaction times, they may experience motion blur.
VA LCDs offer the best contrast ratios among the three types of LCDs. Additionally, they have viewing angles that are wider than TN LCDs but smaller than IPS LCDs. Because of their slower response times, VA LCDs may exhibit ghosting effects.
Advantages of LCDs:
LCDs provide several advantages over other display technologies. One of their main advantages is how little electricity LCDs consume. Due to their lower power consumption than other display types, they are ideal for battery-powered gadgets. LCDs are ideal for situations where accurate and clear images are required because to their high resolution and picture quality. Another advantage of LCDs is how easy it is to integrate them into a range of devices due to their lightweight and compact design.
Disadvantages of LCDs:
Along with their benefits, LCDs also have certain disadvantages. One of LCDs’ main flaws is their narrow viewing angles. This may result in colour distortion and poor image quality when not seen directly on. Additionally, LCDs have poor reaction times, which can result in phenomena like ghosting and motion blur. Another problem is the inability of LCDs to display genuine blacks, which might result in greyish blacks.
Future of LCDs:
Continuous research and development is being done to advance LCD technology. One potential advancement in LCD technology is quantum dots, which can improve colour reproduction and brightness. Another potential development is the adoption of Organic Light-Emitting Diodes (OLEDs), which offer deeper blacks and greater contrast ratios than LCDs.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, LCDs are a crucial component of contemporary technology. They have a number of benefits over other types of displays, including high resolution, energy efficiency, and lightweight construction. They do, however, have some drawbacks, including restricted viewing angles, sluggish response times, and trouble displaying deep blacks. Continuous research and development is being done to advance LCD technology, and potential innovations like Quantum Dots and OLEDs hold promise for LCDs in the future.
Also Read: