Here in this article we will see about Structure of a TFT LCD.
I. Introduction
TFT (Thin Film Transistor) LCD (Liquid Crystal Display) is one of the most widely used display technologies in modern electronics, such as smartphones, tablets, laptops, and televisions. A thin layer of transistors and liquid crystals is used as the projection surface for the images on this type of flat-panel display. High resolution, low power consumption, and high contrast ratio are just a few advantages that TFT technology has over other display technologies. The structure of TFT LCDs must be understood by anybody who wants to work in the display business, create electronics that use TFT LCDs, or simply understand more about the technology underlying their own electronics.
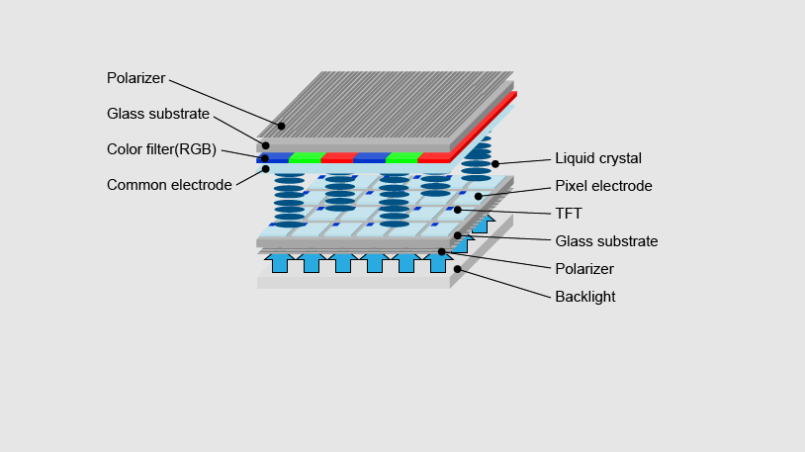
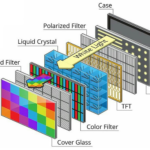
The glass substrate, TFT array, colour filters, liquid crystal layer, and backlight unit are just a few of the fundamental parts of a TFT LCD that will be explained in this blog post. We’ll go through how each of these parts functions as well as how they all come together to create the images we see on a TFT LCD. In addition to designers and engineers, consumers who wish to make educated selections when buying electrical devices with TFT LCD displays should also be aware of the structure of TFT LCDs. Let’s explore TFT LCD technology in more detail now with that in mind.
II. Basic Components of a TFT LCD
A. Glass substrate:
The foundation of a TFT LCD is its glass substrate. Flat, transparent, and fairly thin glass serves as the foundation for all the other components. The glass substrate is often made of a special type of glass that can withstand the stresses of production and everyday usage because it has excellent transparency, a low thermal expansion coefficient, and strong mechanical strength. Smooth areas of the glass substrate can be used for the deposition of the thin-film transistors (TFTs) and other layers that comprise the TFT LCD.
B. Thin-film transistor (TFT) array:
In a TFT LCD, the TFT array serves as the active matrix. Thanks to the many millions of small transistors that make up the gadget, each pixel on the screen may show a variety of colours and intensities. This is made possible by them by managing the voltage applied to the liquid crystal layer. To make the TFTs on the glass substrate, a complex manufacturing process is used to deposit thin layers of semiconductors, insulators, and conductors in a certain pattern and order.
C. Color filters:
On the glass substrate above the TFT array, thin coatings of dye or pigment are used as colour filters. They offer the red, green, and blue (RGB) hues required to create a full-color image on the screen while filtering the light from the backlight unit. To produce a full colour image, each colour filter is lined up with a corresponding TFT pixel.
D. Liquid crystal layer:
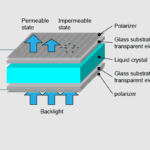
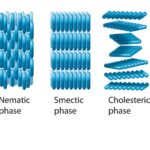
The TFT LCD’s liquid crystal layer is its brains. Between the glass substrate containing the TFTs and the colour filters lies a thin film of liquid crystal material. The voltage that the TFTs apply to the liquid crystals controls their alignment and the polarisation of the light that passes through them. To produce the image on the screen, the liquid crystal layer functions as a shutter, letting light through only when it is specifically needed.
E. Backlight unit:
An essential part of the TFT LCD, the backlight unit supplies the light required to illuminate the liquid crystal layer and produce the image on the screen. A light source, reflectors, light guides, and diffusers are typically included. White LED (light-emitting diode) arrays are frequently used as the light source since they produce strong, even illumination throughout the entire screen. Diffusers assist disperse the light evenly and minimise hotspots, while reflectors and light guides help direct light towards the liquid crystal layer.
In conclusion, the glass substrate, TFT array, colour filters, liquid crystal layer, and backlight unit are the fundamental parts of a TFT LCD. The images we see on the screen are made possible by each of these elements, each of which is essential. Designing and producing high-quality TFT LCD screens requires an understanding of how these parts interact.
III. Conclusion
In conclusion, anyone working in the display technology industry has to grasp the construction of TFT LCDs. The several parts of a TFT LCD work together to display high-quality pictures and movies. The performance of the display as a whole depends on the glass substrate, TFT array, colour filters, liquid crystal layer, and backlight unit, among other components.
It is feasible to design and produce TFT LCDs that specifically address the requirements of diverse applications by understanding how each component functions and the significance of each component. Also, understanding the components might aid in identifying and resolving display issues.
TFT LCDs are used in many different products nowadays, ranging from televisions and computer monitors to smartphones and tablets. The design of TFT LCDs is likely to undergo significant evolution and refinement as technology develops.
In conclusion, a thorough understanding of TFT LCD structure is essential for both the advancement of display technology and the sustained expansion of numerous sectors. Future displays are likely to be even more stunning due to ongoing research and development.
Now we will understand each of this component in depth:
Understanding of Glass substrate in TFT LCD
Understanding of Thin-film transistor (TFT) array in LCD
Understanding of Color filters in TFT LCD
Understanding of Liquid crystal layer in TFT LCD
Understanding of Backlight unit in TFT LCD
Also visit below page: